Acupuncture (Zhen Jiu – 针灸), is based on the concept of “meridians”. It is a precise network of “vessels” through which the flow of “energy” (Qi 氣 in traditional Chinese) travels. There are several types of meridians:
These meridians are connected to the five main organs (Spleen, Lung, Kidneys, Liver, and Heart), transporting the energy produced by these organs throughout the body to maintain vitality.
Acupuncture points are located along those meridians. They can be compared to the switches in a room, while the organs are like light bulbs. In traditional acupuncture, the needle is the ideal tool for stimulating those “switches”. Acupunture is the “finger” that pushes the switch. As an energy-conducting metal, the needle penetrates to different depths.
Using the specific diagnostic methods of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the practitioner identifies energy imbalances linked to the Organs. By stimulating the appropriate acupuncture points, it can act on the energy flows of the meridians to regulate imbalances and promote the harmonious health of its patient.
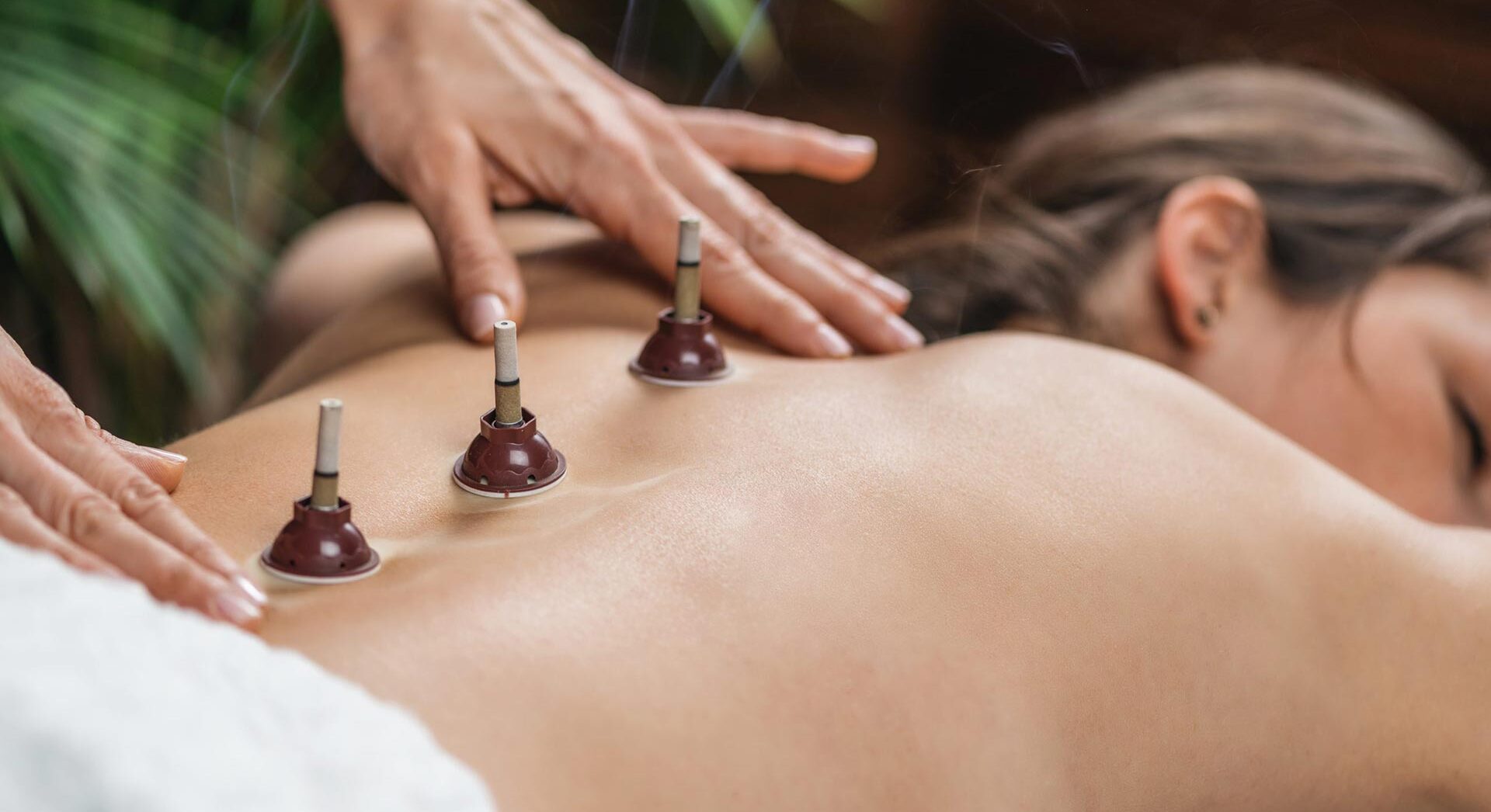
Moxibustion is a therapeutic technique related to acupuncture and is used primarily to relieve pain and eliminate imbalances caused by cold. This ancient practice, complementary to acupuncture, involves specifically heating acupuncture points. When performed professionally, there are no side effects.
There are three distinct moxibustion techniques:

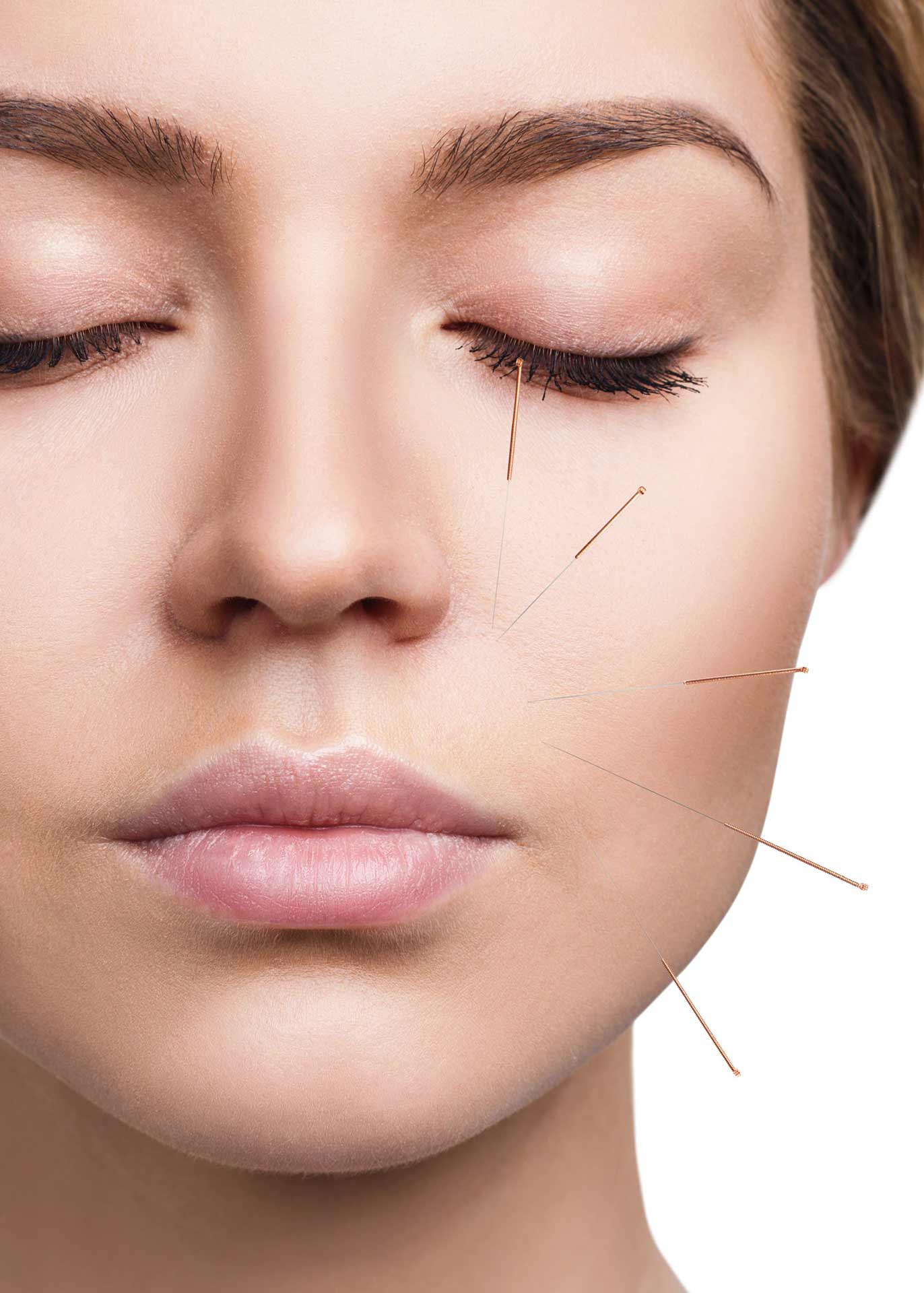
Acu-lifting isa modern, painless technique that uses the science of acupuncture for aesthetic purposes. The needles used are very small, sometimes made of gold or silver. Acu-lifting firms and erases wrinkles by promoting blood flow to facial tissues. Results are quickly visible, but several sessions are necessary for optimal results.
Acupuncture, a medical practice with a history of over 5,000 years, was inscribed on UNESCO’s Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity in 2010. The number of acupuncture points in the human body varies from source to source, ranging from 400 to 700.
Acupuncture is commonly used for surgical procedures, replacing chemical anesthesia. Its effectiveness can be immediate, particularly in emergencies, or delayed to treat chronic illnesses. Several sessions are often required to achieve optimum results.
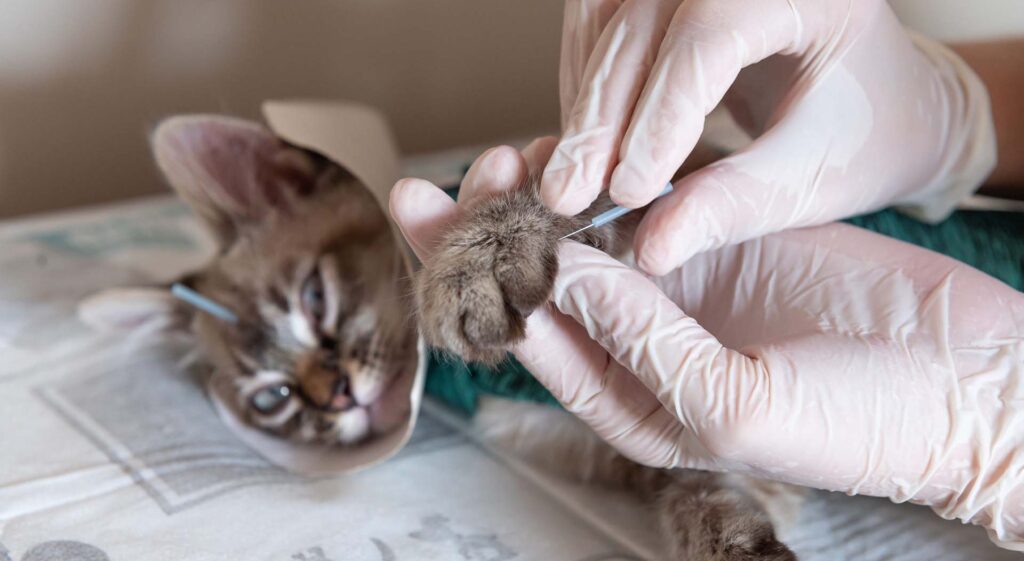
It’s important to note that acupuncture is a therapeutic practice rich in sensations, and acupuncture that elicits sensations is often more effective. It can also be used to treatanimals.
However, it should be emphasized thatacupuncture is not the main therapeutic technique in Chinese medicine, as Chinese Pharmacopoeia is often preferred due to its greater potency.